Introduction: The Virtualization Jungle – Demystifying VDI & “VDA”
With remote and hybrid work becoming the norm, terms like “virtual desktop” and “virtual applications” are everywhere. But what do they actually mean, and more importantly, which one is right for your organization?
We’re diving into the core differences between Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and Virtual Applications (often just called Virtual Apps, or VAD for Virtual Application Delivery). For this post, when we say “Virtual Apps/VDA,” we’re talking about application virtualization—delivering just the application, not the entire desktop. Choosing the right virtualization strategy can save your IT team headaches, boost employee productivity, and keep your budget firmly in check.
VDI: Your Entire Desktop, Wherever You Are (The Full Virtual Experience)
Imagine streaming your entire personal computer—operating system, applications, and data—from a powerful server in a data center or the cloud. Your local device becomes essentially just a screen and keyboard, a window into that remote world.
At its core, VDI relies on hypervisors that create multiple individual virtual machines (VMs), each acting as a full desktop environment. A connection broker then directs users to their personalized digital workspace.
- Persistent VDI acts like your own PC—your settings and files stay.
- Non-persistent VDI gives you a clean desktop at each login—ideal for task-based users.
Perks of VDI:
- Centralized management
- Strong security (data stays on the server)
- Remote access & BYOD support
- Scalability and disaster recovery
Pitfalls of Traditional VDI:
- High upfront costs
- Complexity to deploy and manage
- Heavy reliance on stable, low-latency networks
- Licensing headaches
VDI remains crucial for industries like healthcare, finance, and government, where security and compliance are non-negotiable.
Virtual Applications: Just the App, Please (The Leaner, Meaner Option)
Instead of delivering the whole desktop, Virtual Apps stream only the application interface. The app runs on a remote server, but looks and feels like it’s running locally.
This model emerged from the need to simplify software delivery. Citrix XenApp and Microsoft App-V pioneered this approach, which has since evolved into cloud-native Virtual Application Delivery (VAD).
Perks of Virtual Apps:
- Reduced IT costs
- Simplified app updates and patching
- Enhanced BYOD and remote support
- Better security (apps isolated, no local traces)
Pitfalls of Virtual Apps:
- Not all software can be virtualized
- Upfront server/licensing needs
- A single server crash affects multiple users
Virtual Apps are ideal for task-based workers or organizations that only need a few business-critical apps delivered securely to any device.
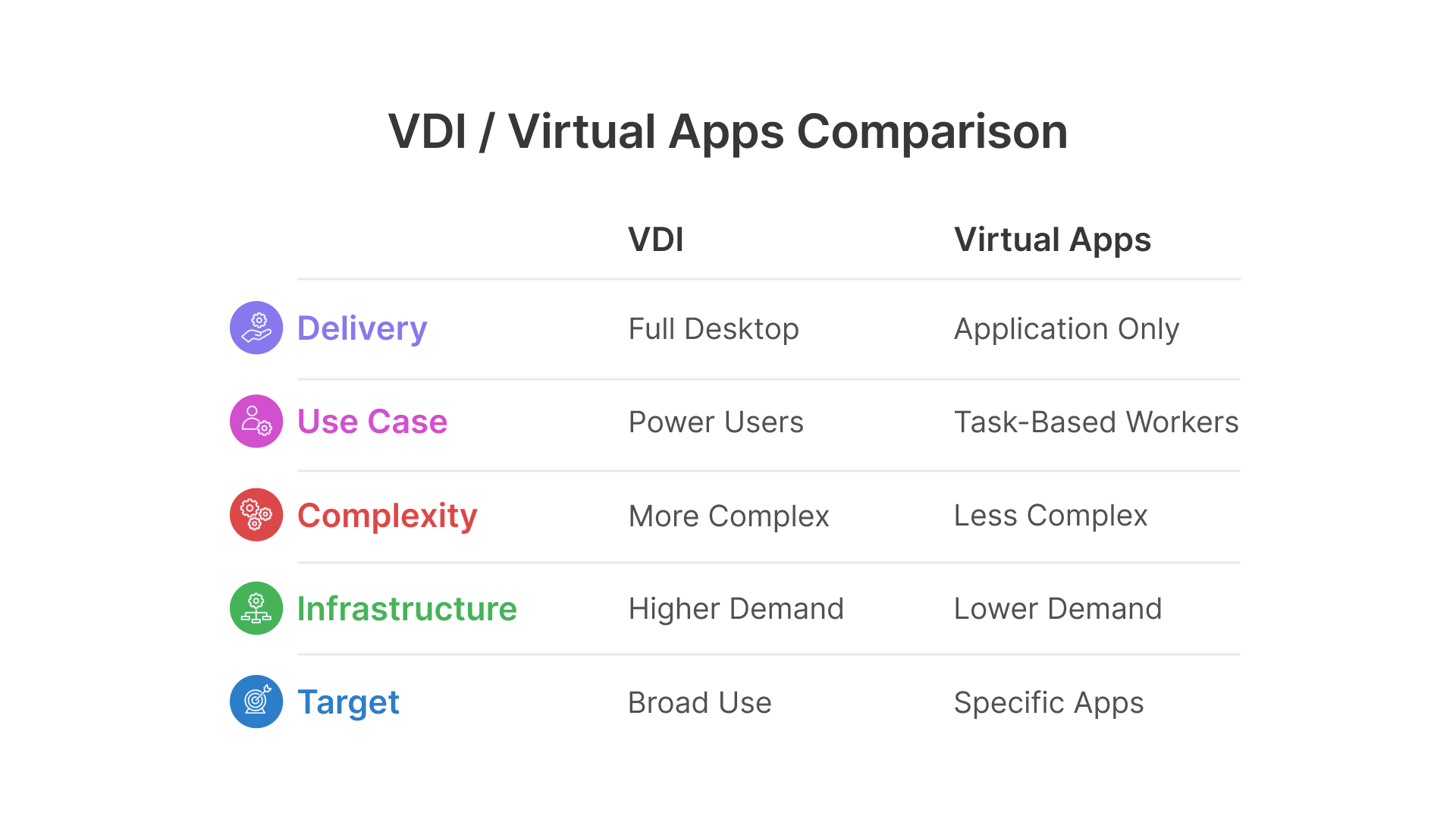
The Showdown: VDI vs. Virtual Apps
- VDI = Full Desktop Immersion → suited for power users, regulated industries, or broad remote workforces.
- Virtual Apps = Lightweight Delivery → suited for specific app-based workflows, agile teams, and cost-sensitive deployments.
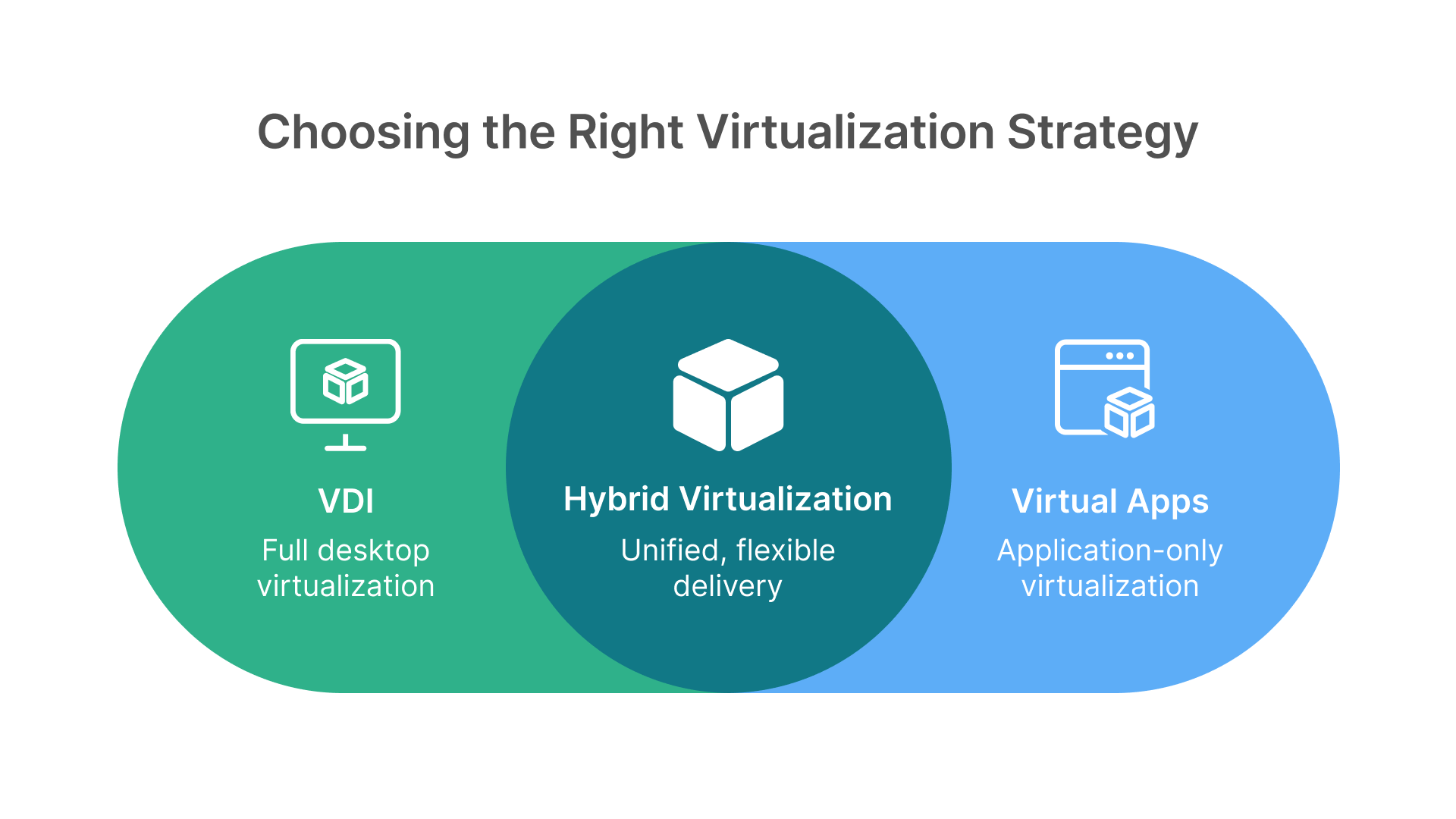
Most enterprises adopt a hybrid approach—VDI for some, Virtual Apps for others—tailoring solutions by role and department.
The Elephants in the Room: Shared Hurdles
Both models share common challenges:
- Upfront infrastructure costs
- Latency & reliance on robust networks
- Complex licensing
- Not all apps virtualize easily
- Security risks if central systems are attacked
These issues make ROI and TCO analysis essential before making decisions.
Thinfinity VDI & Virtual Apps on Oracle Cloud: Overcoming the Hurdles
The challenges of both VDI and Virtual Apps—upfront infrastructure costs, network dependency, complex licensing, limited app support, and centralized security risks—are precisely what Thinfinity Workspace on Oracle Cloud was designed to overcome.
- Reducing Infrastructure Costs: Thinfinity runs natively on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) without requiring extra hypervisors, brokers, or automation layers. This cloud-native approach lowers capital expenditures and simplifies operations, shifting costs into a predictable OPEX model.
- Solving Latency & Performance Issues: By leveraging OCI’s global datacenter footprint, Thinfinity minimizes latency for distributed workforces. Features like protocol optimization and support for GPU workloads ensure even graphics-intensive apps perform like they’re local.
- Simplifying Licensing: Unlike Citrix or VMware’s complex, add-on-driven models, Thinfinity offers concurrent user licensing with all core features included—transparent, scalable, and free of hidden costs.
- Expanding Application Compatibility: Thinfinity supports both full desktops (VDI) and single applications (Virtual Apps), including legacy Windows applications delivered via browser with VirtualUI integration. This flexibility ensures that even hard-to-virtualize apps can be securely delivered.
- Strengthening Security Beyond Centralization: Built on a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) model, Thinfinity enforces MFA, device posture checks, and identity federation (SAML, OAuth, AD, Entra ID). This minimizes the risk of central attacks while maintaining granular access control.
Conclusion: A Smarter Path Beyond the Virtualization Dilemma
The debate between VDI and Virtual Apps has shaped IT strategies for more than a decade, and while each model offers clear benefits, the shared challenges—cost, complexity, performance, and security—have often limited their full potential.
What organizations need today is not another compromise between the two, but a unified solution that eliminates traditional barriers. Thinfinity Workspace on Oracle Cloud delivers exactly that: the flexibility of VDI, the efficiency of Virtual Apps, and the scalability of a cloud-native platform—all while reducing costs and strengthening security with Zero Trust enforcement.
For CIOs, CISOs, and IT leaders tasked with enabling a secure, modern workplace, Thinfinity on OCI represents more than a virtualization platform—it’s a strategic enabler of digital transformation, ensuring that every user, application, and desktop can be delivered seamlessly, securely, and cost-effectively.
The future of work demands agility and resilience. With Thinfinity VDI and Virtual Apps on Oracle Cloud, enterprises can stop choosing between VDI and Virtual Apps—and start embracing both, without compromise.